Dogs are beloved companions and members of our families. However, it is important to be aware that dogs can transmit certain diseases to humans. This essential guide will provide valuable information on the various dog diseases transmitted to humans, their symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options.
Canine Parvovirus (CPV)
The first in the list of dog diseases transmitted to humans is Canine parvovirus. Canine Parvovirus (CPV), often referred to as “parvo,” is a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening viral infection that affects dogs, primarily puppies and unvaccinated dogs. This virus belongs to the Parvoviridae family and can manifest in two primary forms: intestinal and cardiac.
CPV is typically spread through direct contact with infected feces, contaminated environments, or even indirectly through contaminated objects, such as food and water dishes, collars, or human hands. Dogs can contract the virus when they come into contact with the virus and then ingest or inhale it.
The symptoms of CPV can be severe and include lethargy, loss of appetite, vomiting, severe diarrhea (often bloody), dehydration, and high fever. In the cardiac form, symptoms may include sudden death, especially in very young puppies.
This disease can also be transmitted to humans, although this is rare. In humans, symptoms may include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. To prevent CPV transmission, it is crucial to vaccinate dogs and maintain good hygiene practices.
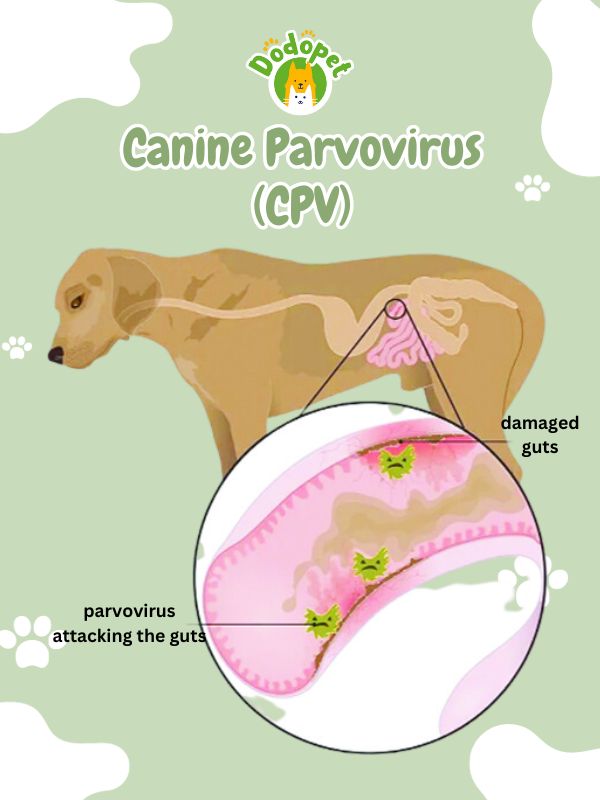
Canine Parvovirus (CPV) – Dog Diseases Transmitted to Humans
How to Prevent Canine Parvovirus Transmission
- Vaccination: The most effective way to prevent CPV is through proper vaccination. Puppies should start a series of vaccinations at around six weeks of age and receive booster shots every few weeks until they are about four months old. Adult dogs should continue to receive regular vaccine boosters to maintain immunity. Consult your veterinarian for a vaccination schedule.
- Isolation: If you have a dog that is suspected of having CPV or has been diagnosed with the virus, isolate the infected dog from other dogs to prevent the virus from spreading. Use a separate living space, feeding and watering dishes, and designate a separate area for elimination.
- Hygiene and Sanitization: Properly clean and disinfect your dog’s living space, toys, bedding, and other items regularly. CPV is resistant to many common disinfectants, so you should use a bleach solution to thoroughly clean contaminated areas and objects. Dilute one part bleach with 30 parts water and let it sit on surfaces for at least 10 minutes before rinsing.
- Hand Washing: Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling any dog, especially if you’ve been in contact with an infected dog or its feces. Use disposable gloves if necessary.
- Avoid High-Risk Environments: Limit your dog’s exposure to areas where CPV may be prevalent, such as dog parks or areas with a high concentration of unvaccinated dogs.
Rabies
Rabies is one of the deadly viral dog diseases transmitted to humans that affects the central nervous system of mammals, including dogs and humans. It is primarily transmitted through the bite or scratch of an infected animal, most commonly dogs. Rabies can be fatal if left untreated. Symptoms in dogs include behavioral changes, excessive drooling, aggression, and paralysis.
In humans, symptoms may include fever, headache, muscle weakness, and confusion. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent rabies in both dogs and humans.
Rabies is most commonly associated with wild animals like bats, raccoons, skunks, foxes, and coyotes. In some areas, stray dogs and feral cats can also be carriers of the virus. Domestic animals like dogs and cats can get infected if they come into contact with wildlife carrying the virus.
The symptoms of rabies can vary but often include initial flu-like symptoms, followed by neurological symptoms such as confusion, hallucinations, paralysis, and agitation. The disease progresses rapidly, and once clinical signs appear, it is almost always fatal.

Rabies – Dog Diseases Transmitted to Humans
Preventing Rabies Transmission
- Vaccination of Pets: Ensure that your pets, particularly dogs and cats, are up-to-date with their rabies vaccinations. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent rabies in domestic animals. Follow your veterinarian’s recommended vaccination schedule.
- Responsible Pet Ownership: Keep your pets indoors or within a secure and supervised outdoor environment. Don’t allow them to roam freely, as they could come into contact with wildlife carrying the virus.
- Avoid Contact with Wild Animals: Do not approach, touch, or attempt to feed wild animals, even if they seem friendly. This includes raccoons, bats, skunks, foxes, and stray or feral animals. Report any animals displaying unusual behavior to local animal control or wildlife authorities.
- Manage Stray Animals: Encourage local authorities to address issues related to stray and feral animals. Stray dogs and cats can carry the rabies virus, posing a risk to both humans and other animals.
- Prompt Medical Attention: If bitten or scratched by an animal, thoroughly wash the wound with soap and water and seek immediate medical attention. A healthcare provider can assess the risk of rabies exposure and determine if post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is necessary.
Leptospirosis – one of dog diseases transmitted to humans
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease that can affect both humans and animals, including dogs. It is caused by various strains of the Leptospira bacteria and is typically transmitted through contact with infected urine, water, soil, or contaminated environments.
Leptospirosis is often transmitted through contact with the urine of infected animals, including rodents, wildlife, and domestic animals. Dogs can contract the disease by drinking, swimming in, or coming into contact with water sources contaminated with the bacteria.
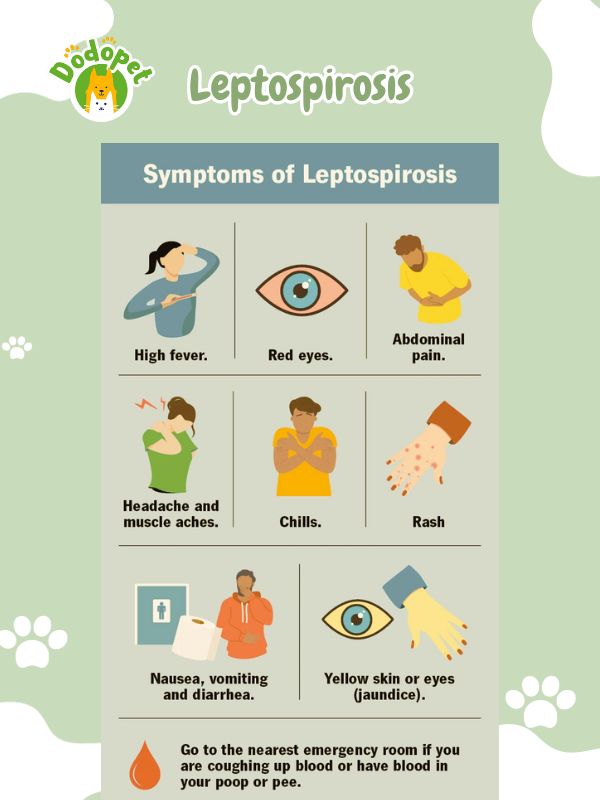
Leptospirosis- Dog Diseases Transmitted to Humans
Preventing Leptospirosis Transmission
- Vaccination: One of the most effective ways to prevent leptospirosis in dogs is through vaccination. Consult your veterinarian about the leptospirosis vaccine, which is often included in combination vaccines. Ensure that your pets are up-to-date with their vaccinations.
- Hygiene and Cleanup: Maintain good hygiene practices when handling pets, including regular handwashing. Clean up after your dogs, and properly dispose of their waste to prevent environmental contamination.
- Avoid Contaminated Water: Be cautious when allowing your dogs to swim or play in bodies of water, especially in areas where leptospirosis is prevalent. Avoid allowing them to drink from stagnant or potentially contaminated water sources.
- Rodent Control: Reduce the risk of exposure by controlling rodents around your property. Rodents can carry the bacteria and serve as reservoirs for leptospirosis.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you suspect that you or your pet may have been exposed to leptospirosis, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for a positive outcome.
Ringworm – one of dog diseases transmitted to humans
Ringworm is one of dangerous dog diseases transmitted to humans. This is a common fungal infection that can affect the skin, hair, and nails of humans and animals, including cats and dogs. Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but by various types of fungi. It is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or animal or by touching contaminated objects or surfaces.
In both humans and animals, ringworm typically presents as a circular, red, and scaly rash. The affected area often becomes itchy. In pets, hair loss can occur, giving the appearance of a “bald spot” within the ring-shaped lesion.
Treatment for ringworm in both dogs and humans typically involves antifungal medications and good hygiene practices.
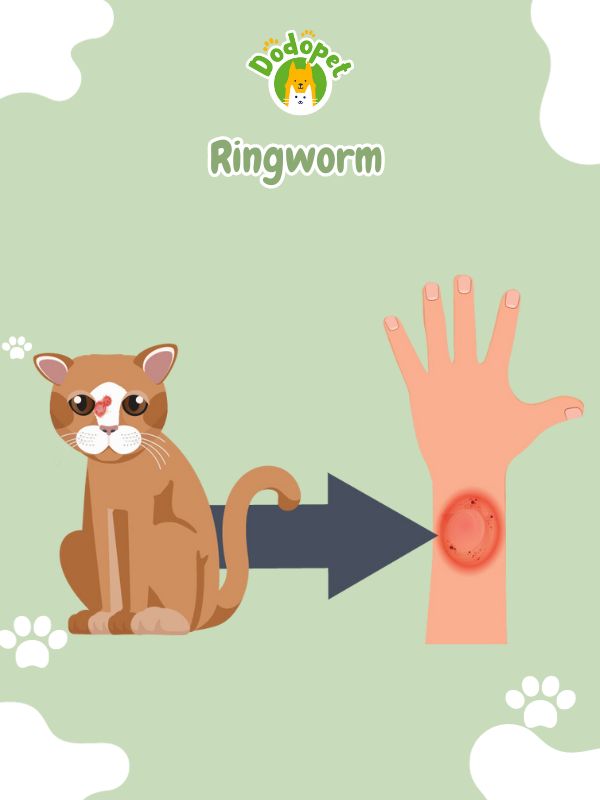
Ringworm – Dog Diseases Transmitted to Humans
Preventing Ringworm Transmission
- Isolate Infected Individuals: If you or your pet is diagnosed with ringworm, it’s essential to isolate the infected individual. Keep them in a separate living space to prevent contact with other family members or pets.
- Hand Hygiene: Practicing good hand hygiene is crucial. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling an infected individual, pet, or any potentially contaminated objects or surfaces.
- Quarantine Infected Pets: Infected pets should be quarantined in a separate area of the home. Avoid direct contact with them, and use disposable gloves when necessary. Clean and disinfect the pet’s living space regularly.
- Disinfection: Regularly clean and disinfect objects and surfaces that may come into contact with an infected individual or pet. Pay special attention to grooming tools, pet bedding, and common living areas.
- Personal Items: Avoid sharing personal items like towels, combs, brushes, and bedding with infected individuals or pets. Each individual should have their own personal items to minimize the risk of transmission.
- Veterinary Care: If you suspect ringworm in your pet, consult with a veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment. Follow the prescribed treatment regimen to ensure complete recovery.
Salmonellosis – one of dog diseases transmitted to humans
One of dangerous dog diseases transmitted to humans is salmonellosis. Salmonellosis is an infectious disease caused by the Salmonella bacteria. It can affect both humans and animals, including pets like dogs and cats. Causes: Salmonellosis is primarily caused by consuming food or water contaminated with Salmonella bacteria. It can also be transmitted through contact with infected animals or their environment.
Salmonellosis is considered a zoonotic disease, which means it can be transmitted from animals to humans and vice versa. People can contract Salmonella from infected pets or their environment.
In humans, salmonellosis can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting, and nausea. These symptoms usually appear within six hours to six days after infection.
Dogs and cats infected with Salmonella may exhibit symptoms such as diarrhea, lethargy, loss of appetite, vomiting, and fever. Some pets may not display symptoms but can still carry and shed the bacteria.

Salmonellosis – Dog Diseases Transmitted to Humans
Preventing Salmonellosis Transmission
- Hygiene: Practice good hand hygiene by washing your hands with soap and water after handling pets, their food, or cleaning their living spaces. This is especially important before eating or preparing food for yourself.
- Avoid Raw Feeding: Refrain from feeding your pets raw or undercooked meat, as it can carry Salmonella bacteria. Opt for commercial pet food or thoroughly cook any homemade pet meals.
- Separate Food Areas: Use separate cutting boards, utensils, and food preparation surfaces for pet food and human food. Keep these areas clean and disinfected.
- Pet Food Safety: Be aware of pet food recalls and follow food safety guidelines. Check for any recalls or warnings related to the pet food you use.
- Limit Contact with Pet Waste: When handling pet waste, wear disposable gloves and promptly clean and disinfect any tools or surfaces that come into contact with it. Wash your hands thoroughly afterward.
Conclusion
While dogs bring joy and companionship to our lives, it is important to be aware of the potential diseases they can transmit to humans. By understanding the risks, symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options for these diseases, dog owners can take the necessary steps to protect both their furry friends and themselves. Regular veterinary care, vaccinations, good hygiene practices, and prompt medical attention are key in preventing the transmission of dog diseases to humans.









