Uncover the hidden dangers of dog gum diseases in our latest blog post. Explore the ins and outs of these dental issues, from their causes and diagnosis to their profound impact on your canine companion’s overall health. Don’t miss this essential guide to safeguarding your furry friend’s well-being. Dive into the world of dog gum diseases and ensure your dog’s smile stays bright and healthy.
What is Dog Gum Diseases?
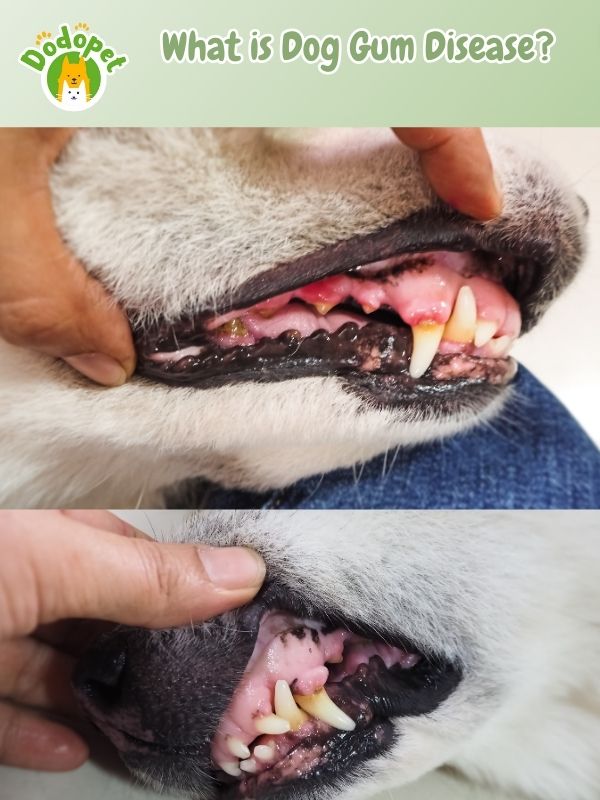
Dog Gum Diseases, also known as canine periodontal disease, is a common dental condition that affects a significant number of dogs, particularly as they age. It is an inflammatory condition that primarily affects the gums and supporting structures of a dog’s teeth. Dog Gum Diseases typically progress in stages and can lead to various oral health issues if left untreated.
What are the Symptoms of Dog Gum Diseases?
The symptoms of Dog Gum Diseases can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common signs to look out for include:
- Red and swollen gums
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Bleeding gums
- Tooth mobility or loss
- Reluctance to eat or chew
- Pawing at the mouth
- Drooling excessively
How are Dog Gum Diseases Diagnosed?
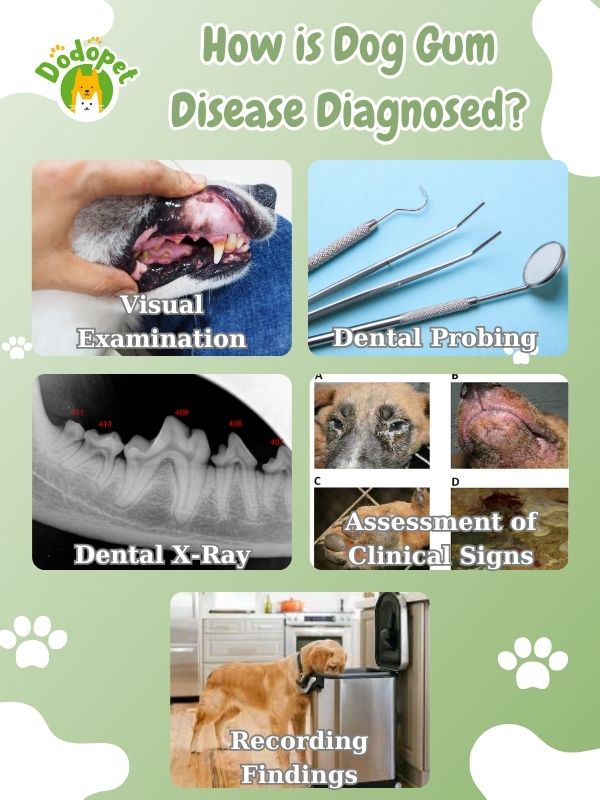
Diagnosing Dog Gum Diseases typically involves a combination of visual examinations, dental probing, and sometimes dental X-rays. Here’s how it’s typically diagnosed:
- Visual Examination: The veterinarian will begin by visually inspecting your dog’s mouth and teeth. They will look for signs of gum disease, including redness, swelling, bleeding, and visible tartar or plaque on the teeth. They may also check for any obvious signs of discomfort or pain in the mouth.
- Dental Probing: To assess the severity of gum disease and identify pockets or gaps between the teeth and gums (a hallmark of periodontal disease), a dental probe is used. This tool allows the veterinarian to measure the depth of these pockets. Deeper pockets are indicative of more advanced stages of gum disease.
- Dental X-Rays: In many cases, dental X-rays are necessary to evaluate the extent of the disease below the gumline. X-rays can reveal issues such as bone loss, tooth root infections, and other dental problems that may not be visible during a visual examination.
- Assessment of Clinical Signs: The veterinarian will also consider clinical signs such as bad breath (halitosis), tooth mobility, reluctance to eat, drooling, and any behavioral changes related to oral discomfort. These signs can help in the diagnosis.
- Recording Findings: The veterinarian will record their findings, including the severity and extent of gum disease, any affected teeth, and any additional dental problems detected.
How are Dog Gum Diseases Diagnosed
What Causes Dog Gum Diseases?
Dog Gum Diseases, also known as canine periodontal disease, is primarily caused by the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar on a dog’s teeth and gums. Several factors contribute to the development and progression of gum disease in dogs:
- Plaque Formation: Plaque is a soft, sticky film that forms on the teeth when food particles and bacteria mix with saliva. Over time, if not removed through regular dental care, plaque can harden into tartar (also called dental calculus).
- Bacterial Infection: Plaque and tartar provide an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive. These bacteria release toxins that irritate the gums and lead to inflammation, which is the hallmark of gum disease.
- Poor Dental Hygiene: A lack of proper dental care, such as regular tooth brushing, dental chews, or dental toys, allows plaque and tartar to build up. This is one of the primary risk factors for gum disease.
- Diet: The type of food a dog eats can influence their oral health. Soft or sticky foods are more likely to contribute to plaque formation compared to hard kibble, as they can adhere to the teeth.
- Breed and Genetics: Some dog breeds are more prone to gum disease due to genetic factors. Breeds with short noses (brachycephalic breeds) may have crowded teeth, making them more susceptible.
- Age: As dogs age, they become more susceptible to gum disease. Senior dogs may be at a higher risk due to a lifetime of plaque buildup.
- Preexisting Dental Conditions: Dogs with dental anomalies or abnormalities, such as misaligned teeth or retained baby teeth, may be at an increased risk of gum disease.
- Systemic Health Conditions: Certain systemic health conditions, such as diabetes and autoimmune diseases, can weaken a dog’s immune system and make them more susceptible to gum disease.
- Tobacco Smoke Exposure: Exposure to secondhand smoke has been associated with an increased risk of gum disease in dogs.

What Causes Dog Gum Diseases
How Dog Gum Diseases Impact Canine Health
Dog Gum Diseases, or canine periodontal disease, can have a significant impact on a dog’s overall health and well-being. The effects of gum disease extend beyond just the mouth and can lead to various health problems if left untreated. Here are some ways in which gum disease can impact canine health:
- Oral Pain and Discomfort: As gum disease progresses, it can cause gum inflammation, infection, and the loss of tooth-supporting structures. This leads to pain and discomfort in the mouth, making it difficult for the dog to eat, chew, or even play with toys.
- Tooth Loss: Advanced gum disease can result in loose or missing teeth. This not only affects a dog’s ability to eat and enjoy food but can also impact their self-esteem and overall quality of life.
- Difficulty Eating: Dogs with gum disease may experience pain and discomfort while eating. This can lead to decreased appetite, weight loss, and malnutrition, which can further affect their health.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): Persistent bad breath is a common sign of gum disease in dogs. While this is primarily a cosmetic issue, it can also be a sign of underlying health problems.
- Bacterial Spread: The bacteria that thrive in the mouth due to gum disease can enter the bloodstream and spread to other parts of the body. This can potentially lead to systemic health issues, including heart disease, kidney disease, and liver disease.
- Heart Health: There is evidence to suggest a link between gum disease and heart disease in dogs. Bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream and affect the heart valves, leading to serious cardiac issues.
- Respiratory Problems: Inhaling bacteria from the mouth can contribute to respiratory problems, especially in dogs with existing lung issues or compromised immune systems.
- Systemic Inflammation: Chronic inflammation associated with gum disease can have a negative impact on the dog’s overall health, contributing to conditions like arthritis and diabetes.

How Dog Gum Diseases Impact Canine Health
The Connection between Canine Gum Disease and Heart Disease
Researchers and investigators in veterinary medicine have explored the connection between canine gum disease (periodontal disease) and heart disease. Although they are still exploring a direct causal link, there is evidence to suggest a potential association between these two conditions in dogs. Here’s what we know about the connection between canine gum disease and heart disease:
- Bacterial Spread: Dogs with advanced gum disease can introduce oral cavity bacteria into the bloodstream through inflamed gum tissues. These bacteria can then circulate throughout the body, including the heart.
- Inflammation: Chronic gum disease inflames the gums and the surrounding tissues. This chronic inflammation can lead to systemic inflammation, experts believe that it contribute to the development and progression of heart disease.
- Heart Valve Infection: In some cases, the bacteria linked to gum disease can attach to the heart valves, causing infective endocarditis. This condition is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves and can be a serious and potentially life-threatening issue.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Studies have indicated that dogs with advanced periodontal disease might face a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases like heart murmurs and congestive heart failure.
- Inflammatory: Some studies have detected elevated levels of specific inflammatory markers in the bloodstream of dogs with gum disease, which can be associated with heart disease.

The Connection between Canine Gum Diseases and Heart Diseases
Preventing Dog Gum Diseases
Preventing Dog Gum Diseases is essential for maintaining your pet’s oral health. Here are some steps you can take to prevent gum disease in dogs:
Regular Brushing
Brushing your dog’s teeth regularly is one of the most effective ways to prevent gum disease. Use a toothbrush and toothpaste specifically designed for dogs, and make sure to brush all surfaces of the teeth and along the gumline.
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet that is rich in nutrients can help support your dog’s oral health. Avoid feeding your dog sugary or sticky foods, as these can contribute to plaque buildup.
Dental Chews and Toys
Giving your dog dental chews and toys can help remove plaque and tartar from their teeth. Look for products that are specifically designed to promote dental health.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular visits to the veterinarian are important for monitoring your dog’s oral health. Your vet can perform professional cleanings and provide guidance on maintaining good dental hygiene at home.
Professional Dental Cleanings
In addition to regular brushing, it’s advisable to opt for professional dental cleanings to effectively remove stubborn tartar and plaque. These cleanings are typically conducted under anesthesia to guarantee a comprehensive examination and thorough cleaning of both the teeth and gums.

Preventing Dog Gum Disease
Treatment Options for Dog Gum Diseases
If your dog is diagnosed with gum disease, there are several treatment options available:
Professional Dental Cleaning
Veterinarians typically initiate the treatment of gum disease with a professional dental cleaning. During this procedure, they will remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and below the gumline. To ensure your dog’s comfort and safety, this may involve the administration of anesthesia.
Antibiotics
In some cases, veterinarians may prescribe antibiotics to control the infection and reduce gum inflammation. These medications can be administered either orally or through a gel directly applied to the gums.
Extraction of Diseased Teeth
When gum disease reaches an advanced stage and affected teeth cannot be saved, veterinarians may opt for extraction. This procedure is essential to prevent further infection and alleviate your dog’s pain and discomfort.
Periodontal Surgery
Advanced gum disease may necessitate periodontal surgery to remove infected tissue and repair damaged gums. Typically, a specialist in veterinary dentistry will perform this procedure.
Home Care
After treatment, it is important to continue practicing good dental hygiene at home. This includes regular brushing, providing dental chews and toys, and maintaining a healthy diet.

Treatment Options for Dog Gum Diseases
Conclusion
Dog Gum Diseases is a common condition that can have serious implications for a dog’s overall health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease, pet owners can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. Regular dental care, including brushing, professional cleanings, and veterinary check-ups, is essential for maintaining a dog’s oral health and overall well-being.