Understanding Common Dog Diseases Skin: Protecting Your Companion Dog. To protect your canine friend’s health, learn about the most common skin problems that affect dogs, as well as their causes, symptoms, and successful treatment.
Learn the causes and symptoms of common dog diseases skin
From the subtlest of irritations to more pronounced afflictions, understanding the spectrum of common dog diseases skin is pivotal in ensuring a life of vitality and contentment for our furry friends.
Learn about FAD which is one of the dog diseases skin
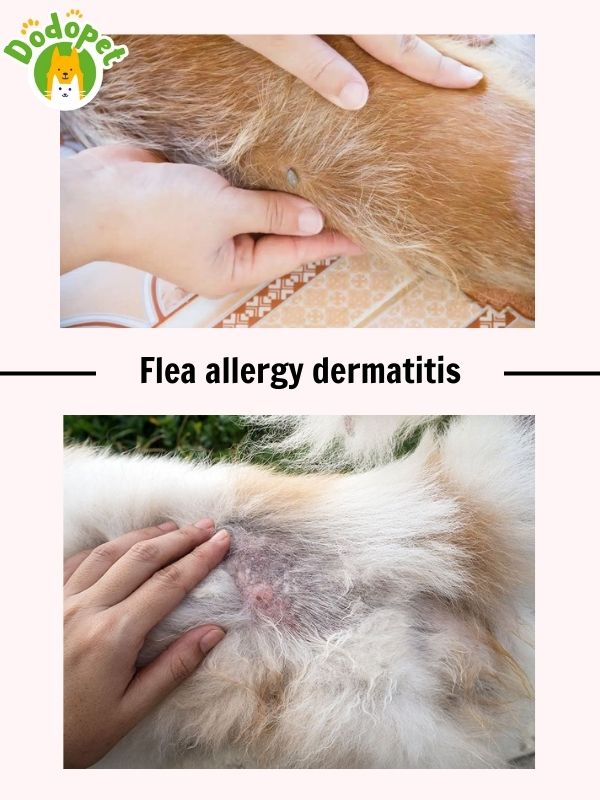
Flea allergy dermatitis (FAD) is one of the most common dog diseases skin caused by an allergy to flea bites.It is one of the most typical reasons dogs scratch and itch. More details on canine flea allergy dermatitis are provided below:
- Causes of Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD): FAD is brought on by an allergic response to flea saliva. Sensitive dogs may react violently with a single flea bite. Immune system of the dog responds to the proteins in flea saliva, which causes the recognizable signs.
- Symptoms of Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD):
– Intense scratching and itching, particularly in the crotch, groin area, lower back, and hindquarters.
– Loss of hair, skin that is red and swollen.
– Scratching too much can cause crusts, open sores, and scabs.
– Due to the injured skin, secondary skin infections could arise, causing extra discomfort.
Learn about FAD which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Atopic Dermatitis which is one of the dog diseases skin
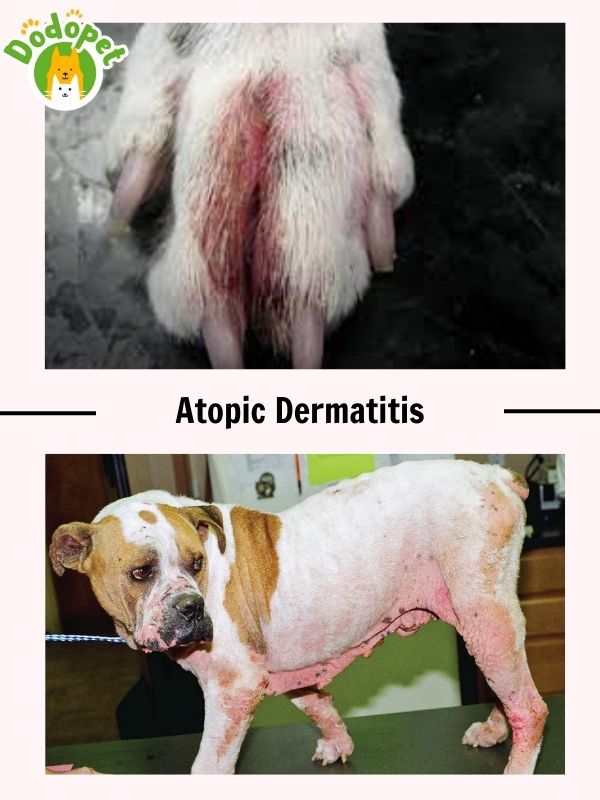
Atopic dermatitis is also one of the most common dog diseases skin. It is a prevalent allergic skin disorder that manifests in dogs as persistent skin inflammation and itching in reaction to many environmental allergens. It is comparable to human eczema and is thought to be one of the primary reasons for scratching and itching in dogs. Atopic dermatitis frequently lasts a lifetime and needs to be carefully managed.
- Causes of Atopic dermatitis (AD):
– Genetic predisposition: dog breeds including Labrador retrievers, bulldogs, and terriers are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
– Environmental allergens: typical triggers include dust mites, mold, grasses, trees, pollen, and animal dander.
– Seasonal and year-round symptoms: some dogs exhibit symptoms primarily during particular seasons, while others may experience problems all year long.
- Symptoms of Atopic dermatitis (AD):
– The primary symptom is pruritus, which is extreme itching. Dogs who over-scratch, chew, lick, or touch their skin can cause skin damage and hair loss.
– Rashes, skin inflammation, and erythema.
– Secondary skin infections as a result of repeated scratching.
– In dogs with atopic dermatitis, recurrent ear infections, or otitis externa, are also typical.
Learn about Atopic Dermatitis which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Contact Dermatitis which is one of the dog diseases skin
When a dog’s skin comes into contact with an irritating or allergic material, contact dermatitis, a skin disorder, develops, it can cause dog diseases skin. In the area of contact, it causes localized inflammation, redness, itching, and discomfort. Dogs can develop contact dermatitis from a variety of things, including plants, chemicals, fabrics, and more, just like humans can.
- Causes of Contact Dermatitis:
– Plants: when a dog rubs up against certain plants, such as poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac, it might result in contact dermatitis.
– Chemicals: the skin of a dog can become irritated by household cleaning products, pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals.
– Fabrics: some fabrics, such as those made of wool or synthetic materials, can irritate and produce friction.
– Metals: metals like nickel, which are used in jewelry, tags, and collars, can cause skin problems.
– Cleaning Agents: contact dermatitis can be brought on by harsh shampoos, soaps, and grooming products.
– Rubber or plastic: some dogs can become irritated locally when exposed to materials like rubber or plastic.
- Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis:
– Swelling, redness, and inflammation in the area of touch.
– Affected area itchiness, scratching, biting, or licking.
– Anguish or pain.
– Hair fall.
– Blisters or, in extreme situations, a rash.

Learn about Contact Dermatitis which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Yeast Infections which is one of the dog diseases skin
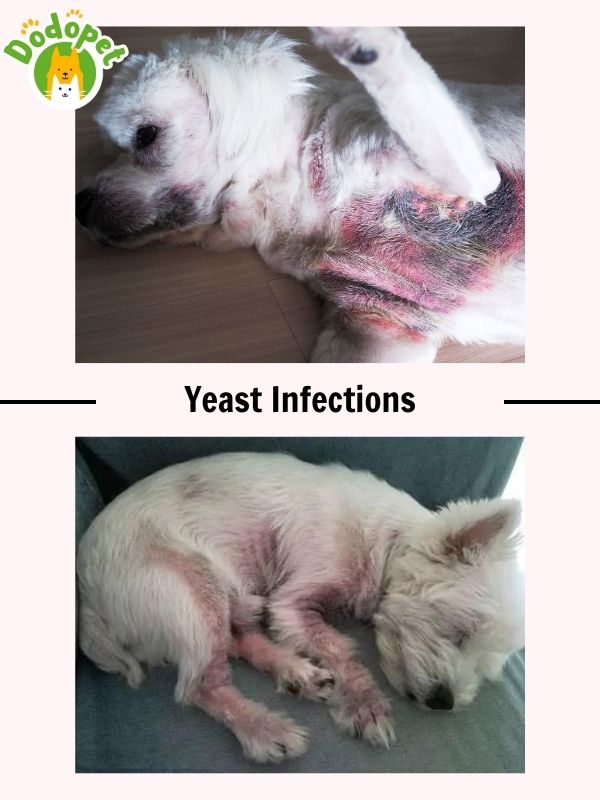
Dogs are susceptible to developing yeast infections, often known as yeast dermatitis or Malassezia dermatitis, which is one of the dog diseases skin. Dogs normally have yeast, a type of fungus, on their skin and in their ears, but an overgrowth can result in an infection. The following details pertain to canine yeast infections:
- Causes of Yeast Infections:
– Moisture and Warmth: warm, moist surroundings are ideal for yeast growth. More prone dogs are those with skin wrinkles, floppy ears, or those who swim frequently.
– Allergies: dogs who have allergies whether they be to food, the environment, or fleas are more likely to get yeast infections.
– Immunodeficiency: dogs with compromised immune systems may be more prone to yeast infections due to underlying medical issues or drugs.
– Poor Grooming: dogs with thick coats that trap moisture or who are not frequently maintained may be more susceptible.
- Symptoms of Yeast Infections:
– Itching: severe scratching and itching that frequently causes redness and inflammation.
– Redness and Inflammation: red, inflamed, and irritated skin may be visible on the area affected.
– Odor: there may be a distinct, frequently unpleasant stench that is comparable to the aroma of popcorn or corn chips.
– Greasy or Oily Skin: the skin may become overly greasy or oily.
– Skin Discoloration: affected areas may become darker or change hue.
– Hair Loss: in some circumstances, hair loss or coat thinning may happen.
– Ear Infections: dogs who have yeast infections may also get ear infections that cause itchiness, discharge, and odor.
Learn about Yeast Infections which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Ringworm which is one of the dog diseases skin
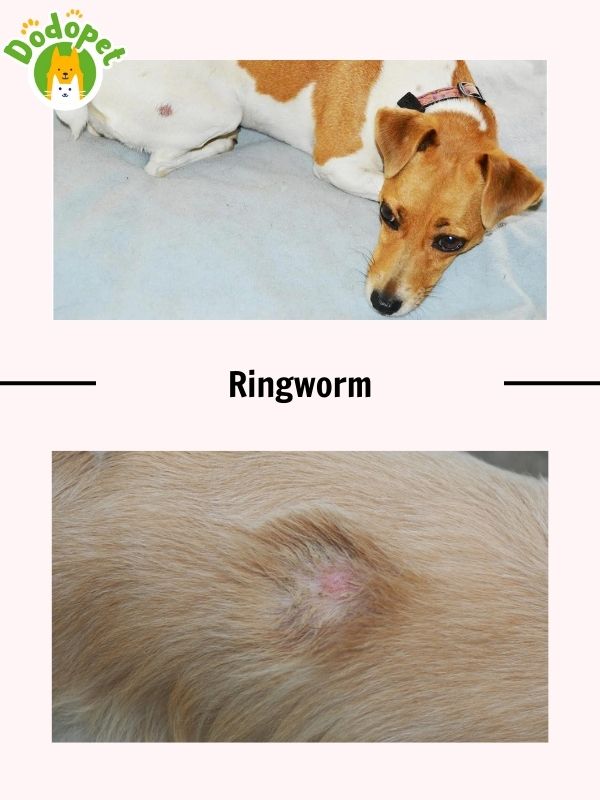
Ringworm fungus causing dermatitis is one of the common dog diseases skin. Despite its name, ringworm is not a worm-related condition. It’s actually a fungal illness that can harm a dog’s skin, hair, and occasionally even nails (as well as humans and other animals). The characteristic circular, red, and occasionally elevated lesions that can appear on the skin are referred to as “ringworm” in medical terminology.
- Causes of Ringworm: various dermatophyte fungus species are the cause of ringworm. These fungi can spread via direct contact with an infected animal or contaminated objects, including as grooming equipment, bedding, and furniture, and they flourish in warm, humid settings.
- Symptoms of Ringworm
– Circular Lesions: hair loss and redness typically appear in circular or atypically shaped patches. The affected region could be crusted or scaly.
– Itching: in the affected areas, some dogs may itch or feel discomfort.
– Broken Hair: infected hairs may become brittle and fall off, giving off a “moth-eaten” appearance.
– Crusty Nails: the nails may occasionally thicken, become brittle, and take on a crusty look.
– Spreading: if the proper precautions are not taken, ringworm lesions may spread to other body parts, other animals, or people.
Learn about Ringworm which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Bacterial Infections which is one of the dog diseases skin
Dogs are susceptible to bacterial infections, which is one of the dog diseases skin that owners need to watch out for. Microorganisms known as bacteria are capable of causing a variety of external and internal ailments. The causes, signs, diagnosis, and treatment of bacterial infections in dogs are covered in the following paragraphs:
- Causes of Bacterial Infections
– Scratches or Wounds: cuts, scratches, or wounds on the skin are entry points for bacteria into the body.
– Weakened Immune System: canines with immune system weaknesses are more prone to bacterial illnesses.
– Moist Environments: bacteria flourish in warm, damp conditions, rendering some body parts susceptible to infection, such as skin folds.
– Allergies: due to continuous scratching and skin irritation, dogs with allergies may be more vulnerable to bacterial infections.
- Symptoms of Bacterial Infections
– Redness and Inflammation: infection-related redness and inflammation can make the infected region look bloated, painful, and red.
– Pus or Discharge: blisters, pustules, or discharge that is filled with pus may be present.
– Itching and Discomfort: infected regions are frequently unpleasant and itchy, which causes scratching or licking.
– Hair Loss: scratching and inflammation surrounding the affected region can lead to hair loss.
– Foul Odor: some bacterial illnesses have an overtly offensive odor.
– Fever: a fever and overall malaise may be brought on by systemic bacterial infections.

Learn about Bacterial Infections which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Hot Spots which is one of the dog diseases skin
Acute moist dermatitis, one of the most common dog diseases skin often known as hot patches or pyotraumatic dermatitis, is a frequent skin ailment in dogs. They can soon develop into skin patches that are swollen, itchy, and frequently painful. Hot spots can cause dogs a lot of discomfort, but with the right care and treatment, they can be properly treated.
- Causes of Hot Spots: Self-trauma frequently results in hot areas. Self-licking or self-scratching frequently have an underlying reason, such as:
– Allergies: allergic reactions to food, environment, or flea bites can cause itching and licking, which might start the formation of hot spots.
– Fleas: flea bites can result in scratching and self-inflicted injury due to their acute itching.
– Moisture and bacteria: whether through swimming, rain, or poor grooming techniques, moist skin or fur can foster the growth of bacteria.
– Underlying Skin Conditions: hot spots may appear more frequently in dogs that have underlying skin conditions like seborrhea or matted fur.
- Symptoms of Hot Spots:
– Inflammation and Redness: the affected area appears inflamed, swollen, and red.
– Moisture: hot regions frequently have moisture because the dog licks or scratches them.
– Hair Loss: because of the self-inflicted injury, the fur may be matted or absent around the hot region.
– Pain and Discomfort: dogs with hot spots often lick, bite, or chew the affected region as a way of expressing their displeasure.
– Oozing and Crusting: because of the inflammation and bacterial involvement, the skin may ooze and develop crusts.
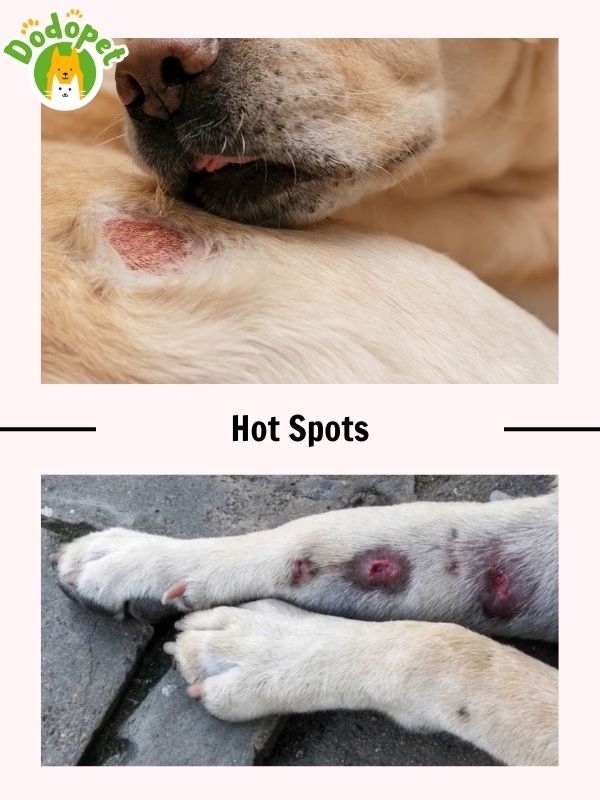
Learn about Hot Spots which is one of the dog diseases skin
Learn about Mange which is one of the dog diseases skin
Mites, which are minuscule parasites that can infest a dog’s skin and fur, are the source of one of the dog diseases skin known as mange. Sarcoptic and demodectic mange are the two main kinds of mange that typically affect dogs. Both kinds can irritate skin to varied degrees of discomfort.
- Causes of Mange: infestations of mites, which are microscopic parasitic arachnids, lead to mange in dogs. Mange can be brought on by a variety of mite types, each of which has its own causes and risk factors.
- Symptoms of Mange: depending on the type of mange and the extent of the infection, the symptoms of mange in dogs might change. A veterinarian’s accurate diagnosis is crucial since several kinds of mange mites can produce symptoms that are identical to one another.
We set out on a voyage through the world of dog diseases skin in this in-depth manual. We examine the underlying causes of skin conditions, the wide range of maladies that can afflict dogs, and provide you with knowledge about how to spot symptoms. This guide attempts to arm dog owners with the knowledge necessary to negotiate the complex landscape of canine skin health, whether it is the constant itching of allergies, the enduring discomfort of infections, or the cryptic problems of dermatological illnesses. Join us as we explore the mysteries that lay beneath the surface and set out on a mission to provide our beloved pets with skin that is healthier and happier.

Learn about Mange which is one of the dog diseases skin
Comprehensive guide to diagnosis and treatment of dog diseases skin
It takes a mix of close observation, diagnostic exams, and proper management to identify and treat dog diseases skin. Here is a description of the procedure:
Unraveling the diagnostic process of dog diseases skin
A thorough diagnosis procedure is essential when a dog displays symptoms of a skin issue in order to identify the underlying cause and create an efficient treatment strategy. This step-by-step manual explains how doctors identify dog diseases skin:
- Physical Examination: your dog’s skin and coat will be carefully examined by a veterinarian to begin with. They’ll be on the lookout for particular signs including redness, inflammation, hair loss, itching, and other outward sores.
- Medical History: by telling the vet about your dog’s nutrition, environment, and any recent changes, you might assist the doctor rule out certain causes. This will help reduce the risk of dog diseases skin.
- Skin scraping: in order to gather samples, the damaged skin’s surface is gently scraped. The existence of mites, germs, or yeast is next checked for by microscopically examining these samples.
- Cytology: in order to determine the type of microorganisms present, such as bacteria or yeast, swabs or samples of the affected skin may be examined under a microscope.
- Fungal Culture: a sample may be sent to a lab for fungal culture in order to identify the precise type of fungus present in a suspected fungal infection (such as ringworm).
- Allergy Testing: if suspect that your dog has dog diseases skin, the veterinarian may advise testing for allergies, which may involve blood tests or intradermal skin tests to detect particular allergens.
- Biopsy: to get a deeper tissue sample for a more precise diagnosis, a tiny skin biopsy may occasionally be carried out.
Veterinarians may reliably identify skin conditions in dogs by carefully following these processes, which also help them create specialized treatment regimens to improve the condition of the dog diseases skin and overall wellbeing.

Unraveling the diagnostic process of dog diseases skin
Comprehensive treatment approaches in dog diseases skin
The type of dog diseases skin and its underlying cause will determine the best course of treatment. The treatment strategy will be customized to your dog’s condition by your veterinarian. Here are a few typical treatment strategies:
- Medications: medications may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal drugs for fungal infections, or antiparasitic drugs for mite infestations, depending on the diagnosis.
- Topical treatments include medicated shampoos, creams, sprays, and ointments that can be applied locally to treat dog diseases skin.
- Oral Medications: for more widespread or serious illnesses, doctors may give oral antibiotics, antifungal drugs, or other medicines.
- Steroids or Immune Modulators: in some circumstances, steroids or immune modulators may be used to treat inflammation and itching, but due to potential side effects, their usage should be under veterinary supervision.
- Hygiene and Care: to avoid increased irritability and secondary infections, proper grooming, cleansing, and wound care may be advised.
- Environmental Management: to prevent recurrence, it’s critical to address underlying issues like fleas, allergies, or stressors.
- Dietary Management: If there is a suspicion of a food allergy, a dietary adjustment or specialized dietary advice may be given.
- Regular Follow-up: Follow-up visits are necessary because skin disorders may need continuing care. To track development and make any required modifications to the treatment plan, it’s crucial to schedule frequent follow-up sessions with your veterinarian.
Keep in mind that the material presented here is of a broad nature. Based on your dog’s unique condition and demands, a trained veterinarian should decide the precise diagnosis and treatment strategy for the dog diseases skin.

Comprehensive treatment approaches in dog diseases skin
How to prevent dog diseases skin
Combining good cleanliness, routine grooming, a nutritious diet, and a secure environment can help prevent dog diseases skin. The following actions can be taken to help avoid dog diseases skin:
- Regular Grooming: keeping your dog’s skin and coat healthy requires regular grooming. The removal of dirt, debris, and loose hair using a brush helps to prevent skin problems. Additionally, it increases blood flow to the skin, improving skin health in general.
- Bathing: giving your dog a moderate dog shampoo bath at regular intervals will assist to maintain their skin clean and free of debris, allergies, and parasites. Avoid over-bathing, though, since it can deplete the skin of its natural oils and cause dryness.
- Proper Nutrition: feeding your dog a well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet promotes overall health, which includes skin health. Omega-3 and Omega-6 essential fatty acids in particular are crucial for keeping healthy skin and a lustrous coat.
- Flea and Tick Prevention: use the veterinarian-recommended flea and tick preventive products on a regular basis to shield your dog from these parasites, which can lead to infections and skin rashes.
- Allergen Management: identify and control any allergies that may cause skin problems in your dog. Pollen, dust mites, particular meals, or other environmental factors may be among them.
- Regular Vet Check-ups: visits to the veterinarian on a regular basis might aid in spotting and treating skin conditions early on. Your dog’s veterinarian can offer guidance on preventative measures and suggest suitable items for maintaining your dog’s skin health.
- Environmental hygiene: involves keeping your dog’s home environment irritant-free and spotless. Make sure the room is well-ventilated, wash the bedding frequently, and vacuum the carpets.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: use caution when cleaning or using other home goods near your dog. Choose pet-safe cleaning supplies instead than harsh chemicals, which can hurt the skin.
- Proper Hydration: hydration is important, so make sure your dog always has access to fresh, clean water. For general health, including skin hydration, hydration is crucial.
- Exercise and Mental Stimulation: regular exercise and mental stimulation are important for maintaining your dog’s general health, which can be seen in the state of their skin and coat.
- Avoid Overheating: Keep your dog away from excessive temperatures to avoid overheating. Some skin disorders can become worse in the heat.
- Regular Check-ups: Check your dog’s skin often for any changes or anomalies, such as lumps, bumps, redness, or excessive scratching.
Consult your veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and treatment if you detect any changes in your dog’s skin or believe it may have dog diseases skin. Because each dog is different, it’s crucial to customize preventive measures to your dog’s particular requirements and environment.









